Direct inference with XGBoost¶
General¶
XGBoost is avaliable (at least) since CMSSW_9_2_4 cmssw#19377.
In CMSSW environment, XGBoost can be used via its Python API.
For UL era, there are different verisons available for different SCRAM_ARCH:
-
For
slc7_amd64_gcc700and above, ver.0.80 is available. -
For
slc7_amd64_gcc900and above, ver.1.3.3 is available. -
Please note that different major versions have different behavior( See Caveat Session).
Existing Examples¶
There are some existing good examples of using XGBoost under CMSSW, as listed below:
-
Offical sample for testing the integration of XGBoost library with CMSSW.
-
Useful codes created by Dr. Huilin Qu for inference with existing trained model.
-
C/C++ Interface for inference with existing trained model.
We will provide examples for both C/C++ interface and python interface of XGBoost under CMSSW environment.
Example: Classification of points from joint-Gaussian distribution.¶
In this specific example, you will use XGBoost to classify data points generated from two 8-dimension joint-Gaussian distribution.
| Feature Index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μ1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| μ2 | 0 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 6.1 | 8.1 | 11 |
| σ½ = σ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| |μ1 - μ2| / σ | 1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 3 |
All generated data points for train(1:10000,2:10000) and test(1:1000,2:1000) are stored as Train_data.csv/Test_data.csv.
Preparing Model¶
The training process of a XGBoost model can be done outside of CMSSW. We provide a python script for illustration.
# importing necessary models
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from xgboost import XGBClassifier # Or XGBRegressor for Logistic Regression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# specify parameters via map
param = {'n_estimators':50}
xgb = XGBClassifier(param)
# using Pandas.DataFrame data-format, other available format are XGBoost's DMatrix and numpy.ndarray
train_data = pd.read_csv("path/to/the/data") # The training dataset is code/XGBoost/Train_data.csv
train_Variable = train_data['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7']
train_Score = train_data['Type'] # Score should be integer, 0, 1, (2 and larger for multiclass)
test_data = pd.read_csv("path/to/the/data") # The testing dataset is code/XGBoost/Test_data.csv
test_Variable = test_data['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7']
test_Score = test_data['Type']
# Now the data are well prepared and named as train_Variable, train_Score and test_Variable, test_Score.
xgb.fit(train_Variable, train_Score) # Training
xgb.predict(test_Variable) # Outputs are integers
xgb.predict_proba(test_Variable) # Output scores , output structre: [prob for 0, prob for 1,...]
xgb.save_model("\Path\To\Where\You\Want\ModelName.model") # Saving model
ModelName.model is thus available for python and C/C++ api to load. Please use the XGBoost major version consistently (see Caveat). While training with data from different datasets, proper treatment of weights are necessary for better model performance. Please refer to Official Recommendation for more details.
C/C++ Usage with CMSSW¶
To use a saved XGBoost model with C/C++ code, it is convenient to use the XGBoost's offical C api. Here we provide a simple example as following.
Module setup¶
There is no official CMSSW interface for XGBoost while its library are placed in cvmfs of CMSSW. Thus we have to use the raw c_api as well as setting up the library manually.
- To run XGBoost's
c_apiwithin CMSSW framework, in addition to the following standard setup.The addtional effort is to add corresponding xml file(s) toexport SCRAM_ARCH="slc7_amd64_gcc700" # To use higher version, please switch to slc7_amd64_900 export CMSSW_VERSION="CMSSW_X_Y_Z" source /cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/cmsset_default.sh cmsrel "$CMSSW_VERSION" cd "$CMSSW_VERSION/src" cmsenv scram b$CMSSW_BASE/toolbox$CMSSW_BASE/config/toolbox/$SCRAM_ARCH/tools/selected/for setting up XGBoost.
For lower version (<1), add two xml files as below.
xgboost.xml<tool name="xgboost" version="0.80"> <lib name="xgboost"/> <client> <environment name="LIBDIR" default="/cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/$SCRAM_ARCH/external/py2-xgboost/0.80-ikaegh/lib/python2.7/site-packages/xgboost/lib"/> <environment name="INCLUDE" default="/cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/$SCRAM_ARCH/external/py2-xgboost/0.80-ikaegh/lib/python2.7/site-packages/xgboost/include/"/> </client> <runtime name="ROOT_INCLUDE_PATH" value="$INCLUDE" type="path"/> <runtime name="PATH" value="$INCLUDE" type="path"/> <use name="rabit"/> </tool>rabit.xmlPlease note that the path in<tool name="rabit" version="0.80"> <client> <environment name="INCLUDE" default="/cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/$SCRAM_ARCH/external/py2-xgboost/0.80-ikaegh/lib/python2.7/site-packages/xgboost/rabit/include/"/> </client> <runtime name="ROOT_INCLUDE_PATH" value="$INCLUDE" type="path"/> <runtime name="PATH" value="$INCLUDE" type="path"/> </tool>cvmfsis not fixed, one can list all available versions in thepy2-xgboostdirectory and choose one to use.For higher version (>=1), and one xml file
xgboost.xmlAlso one has the freedom to choose the available xgboost version inside<tool name="xgboost" version="0.80"> <lib name="xgboost"/> <client> <environment name="LIBDIR" default="/cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/$SCRAM_ARCH/external/xgboost/1.3.3/lib64"/> <environment name="INCLUDE" default="/cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/$SCRAM_ARCH/external/xgboost/1.3.3/include/"/> </client> <runtime name="ROOT_INCLUDE_PATH" value="$INCLUDE" type="path"/> <runtime name="PATH" value="$INCLUDE" type="path"/> </tool>xgboostdirectory.
-
After adding xml file(s), the following commands should be executed for setting up.
- For lower version (<1), use
scram setup rabit scram setup xgboost - For higher version (>=1), use
scram setup xgboost
- For lower version (<1), use
-
For using XGBoost as a plugin of CMSSW, it is necessary to add
in your<use name="xgboost"/> <flags EDM_PLUGIN="1"/>plugins/BuildFile.xml. If you are using the interface inside thesrc/orinterface/directory of your module, make sure to create a globalBuildFile.xmlfile next to theses directories, containing (at least):<use name="xgboost"/> <export> <lib name="1"/> </export> -
The
libxgboost.sowould be too large to load forcmsRunjob, please using the following commands for pre-loading:export LD_PRELOAD=$CMSSW_BASE/external/$SCRAM_ARCH/lib/libxgboost.so
Basic Usage of C API¶
In order to use c_api of XGBoost to load model and operate inference, one should construct necessaries objects:
-
Files to include
#include <xgboost/c_api.h> -
BoosterHandle: worker of XGBoost// Declare Object BoosterHandle booster_; // Allocate memory in C style XGBoosterCreate(NULL,0,&booster_); // Load Model XGBoosterLoadModel(booster_,model_path.c_str()); // second argument should be a const char *. -
DMatrixHandle: handle to dmatrix, the data format of XGBoostfloat TestData[2000][8] // Suppose 2000 data points, each data point has 8 dimension // Assign data to the "TestData" 2d array ... // Declare object DMatrixHandle data_; // Allocate memory and use external float array to initialize XGDMatrixCreateFromMat((float *)TestData,2000,8,-1,&data_); // The first argument takes in float * namely 1d float array only, 2nd & 3rd: shape of input, 4th: value to replace missing ones -
XGBoosterPredict: function for inferencebst_ulong outlen; // bst_ulong is a typedef of unsigned long const float *f; // array to store predictions XGBoosterPredict(booster_,data_,0,0,&out_len,&f);// lower version API // XGBoosterPredict(booster_,data_,0,0,0,&out_len,&f);// higher version API /* lower version (ver.<1) API XGB_DLL int XGBoosterPredict( BoosterHandle handle, DMatrixHandle dmat, int option_mask, // 0 for normal output, namely reporting scores int training, // 0 for prediction bst_ulong * out_len, const float ** out_result ) higher version (ver.>=1) API XGB_DLL int XGBoosterPredict( BoosterHandle handle, DMatrixHandle dmat, int option_mask, // 0 for normal output, namely reporting scores int ntree_limit, // how many trees for prediction, set to 0 means no limit int training, // 0 for prediction bst_ulong * out_len, const float ** out_result ) */
Full Example¶
Click to expand full example
The example assumes the following directory structure:
MySubsystem/MyModule/
│
├── plugins/
│ ├── XGBoostExample.cc
│ └── BuildFile.xml
│
├── python/
│ └── xgboost_cfg.py
│
├── toolbox/ (storing necessary xml(s) to be copied to toolbox/ of $CMSSW_BASE)
│ └── xgboost.xml
│ └── rabit.xml (lower version only)
│
└── data/
└── Test_data.csv
└── lowVer.model / highVer.model
XGBoosterPredict in analyze rather than beginJob. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | |
Python Usage¶
To use XGBoost's python interface, using the snippet below under CMSSW environment
# importing necessary models
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
xgb = XGBClassifier()
xgb.load_model('ModelName.model')
# After loading model, usage is the same as discussed in the model preparation section.
Caveat¶
It is worth mentioning that both behavior and APIs of different XGBoost version can have difference.
-
When using
c_apifor C/C++ inference, for ver.<1, the API isXGB_DLL int XGBoosterPredict(BoosterHandle handle, DMatrixHandle dmat,int option_mask, int training, bst_ulong * out_len,const float ** out_result), while for ver.>=1 the API changes toXGB_DLL int XGBoosterPredict(BoosterHandle handle, DMatrixHandle dmat,int option_mask, unsigned int ntree_limit, int training, bst_ulong * out_len,const float ** out_result). -
Model from ver.>=1 cannot be used for ver.<1.
Other important issue for C/C++ user is that DMatrix only takes in single precision floats (float), not double precision floats (double).
Appendix: Tips for XGBoost users¶
Importance Plot¶
XGBoost uses F-score to describe feature importance quantatitively. XGBoost's python API provides a nice tool,plot_importance, to plot the feature importance conveniently after finishing train.
# Once the training is done, the plot_importance function can thus be used to plot the feature importance.
from xgboost import plot_importance # Import the function
plot_importance(xgb) # suppose the xgboost object is named "xgb"
plt.savefig("importance_plot.pdf") # plot_importance is based on matplotlib, so the plot can be saved use plt.savefig()
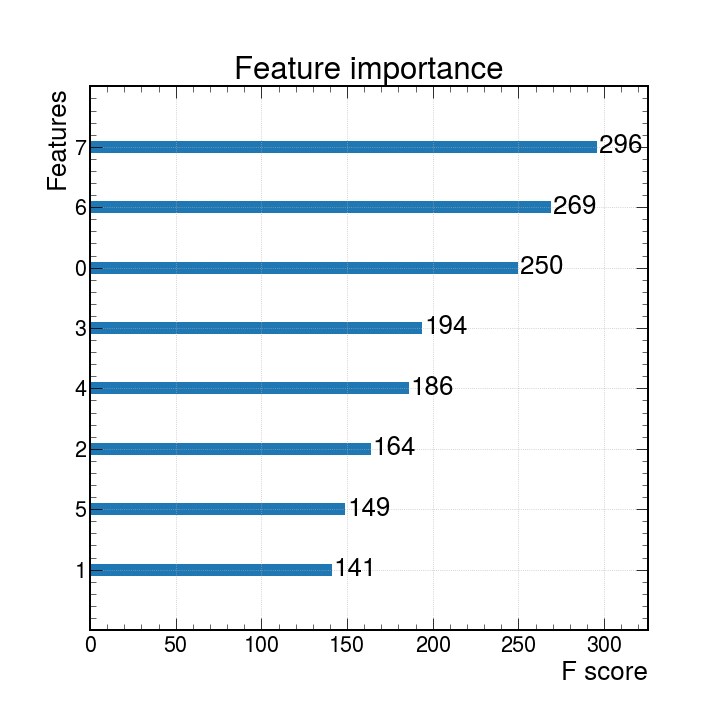 The importance plot is consistent with our expectation, as in our toy-model, the data points differ by most on the feature "7". (see toy model setup).
The importance plot is consistent with our expectation, as in our toy-model, the data points differ by most on the feature "7". (see toy model setup). ROC Curve and AUC¶
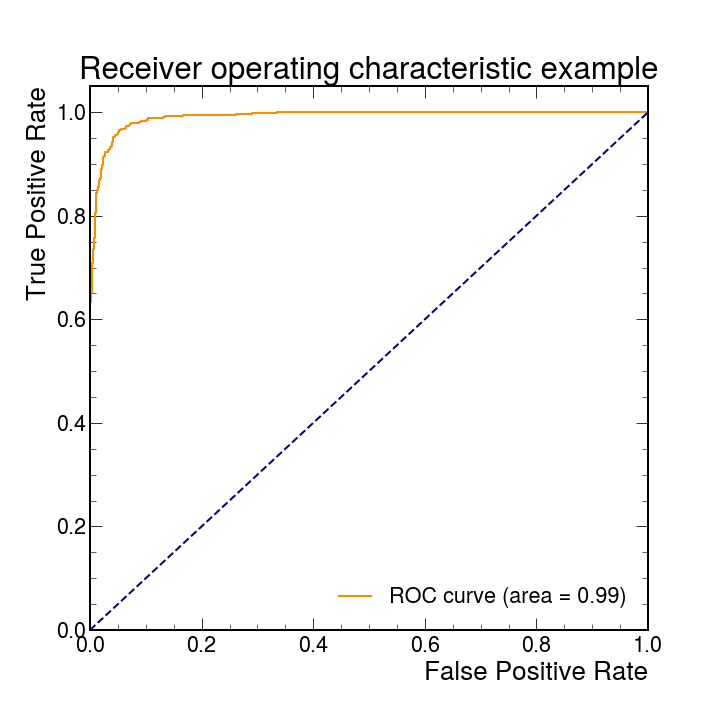
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and auccrency (AUC) are key quantities to describe the model performance. For XGBoost, ROC curve and auc score can be easily obtained with the help of sci-kit learn (sklearn) functionals, which is also in CMSSW software.
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score,roc_curve,auc
# ROC and AUC should be obtained on test set
# Suppose the ground truth is 'y_test', and the output score is named as 'y_score'
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_score)
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.figure()
lw = 2
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange',
lw=lw, label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % roc_auc)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=lw, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('Receiver operating characteristic example')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
# plt.show() # display the figure when not using jupyter display
plt.savefig("roc.png") # resulting plot is shown below
Reference of XGBoost¶
- XGBoost Wiki: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XGBoost
- XGBoost Github Repo.: https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost
- XGBoost offical api tutorial
- Latest, Python: https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/python/index.html
- Latest, C/C++: https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/c_api_tutorial.html
- Older (0.80), Python: https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/release_0.80/python/index.html
- No Tutorial for older version C/C++ api, source code: https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost/blob/release_0.80/src/c_api/c_api.cc