Direct inference with hls4ml¶
hls4ml is a Python package developed by the Fast Machine Learning Lab. It's primary purpose is to create firmware implementations of machine learning (ML) models to be run on FPGAs. The package interfaces with a high-level synthesis (HLS) backend (i.e. Xilinx Vivado HLS) to transpile the ML model into hardware description language (HDL). The primary hls4ml documentation, including API reference pages, is located here.
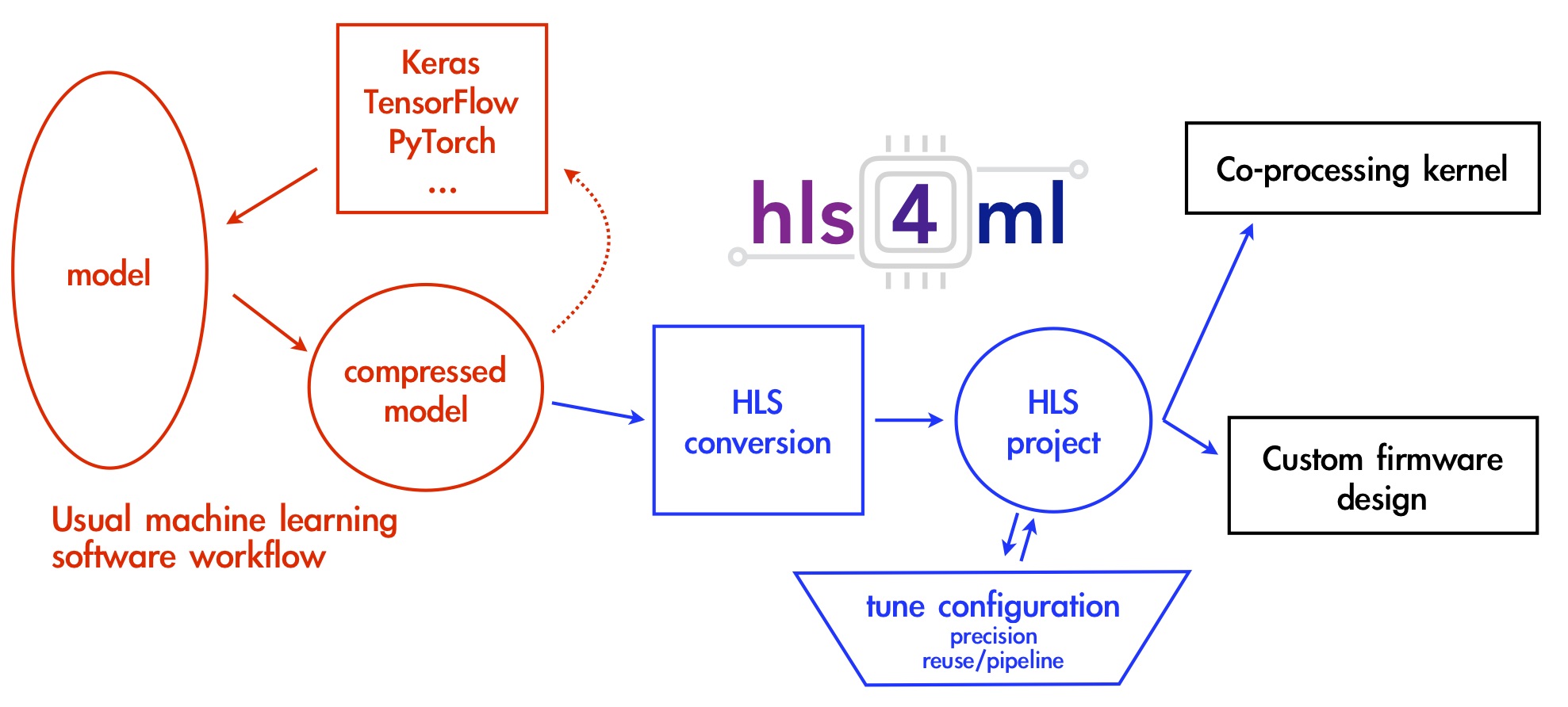
Current tools supported¶
| ML framework/HLS backend | (Q)Keras | PyTorch | (Q)ONNX | Vivado HLS | Intel HLS | Vitis HLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | supported | limited | in development | supported | supported | experimental |
| CNN | supported | limited | in development | supported | supported | experimental |
| RNN (LSTM) | supported | N/A | in development | supported | supported | N/A |
| GNN (GarNet) | supported | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Compile an example model¶
import hls4ml
# Fetch a keras model from our example repository
# This will download our example model to your working directory and return an example configuration file
config = hls4ml.utils.fetch_example_model('KERAS_3layer.json')
# You can print the configuration to see some default parameters
print(config)
# Convert it to a hls project
hls_model = hls4ml.converters.keras_to_hls(config)
# Print full list of example models if you want to explore more
hls4ml.utils.fetch_example_list()
# Use Vivado HLS to synthesize the model
# This might take several minutes
hls_model.build()
# Print out the report if you want
hls4ml.report.read_vivado_report('my-hls-test')
More resources¶
The main hls4ml tutorial code is kept on GitHub. Users are welcome to walk through the notebooks at their own pace. There is also a set of slides linked to the README.
That said, there have been several cases where the hls4ml developers have given live demonstrations and tutorials. Below is a non-exhaustive list of tutorials given in the last few years (newest on top).
